Understanding Asthma and Its Triggers
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition affecting millions worldwide. It leads to inflammation and narrowing of the airways, causing difficulty in breathing. Common symptoms include wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. Triggers vary among individuals but often include allergens, pollution, respiratory infections, and even certain foods.
Asthma treatments: Blue Asthma Inhaler, Red Inhaler for asthma
The Role of Diet in Asthma Management
Diet plays a crucial role in managing asthma. Consuming the right nutrients can help reduce inflammation and strengthen the immune system. Conversely, poor dietary choices can exacerbate asthma symptoms. Let’s explore how specific dietary components impact asthma.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
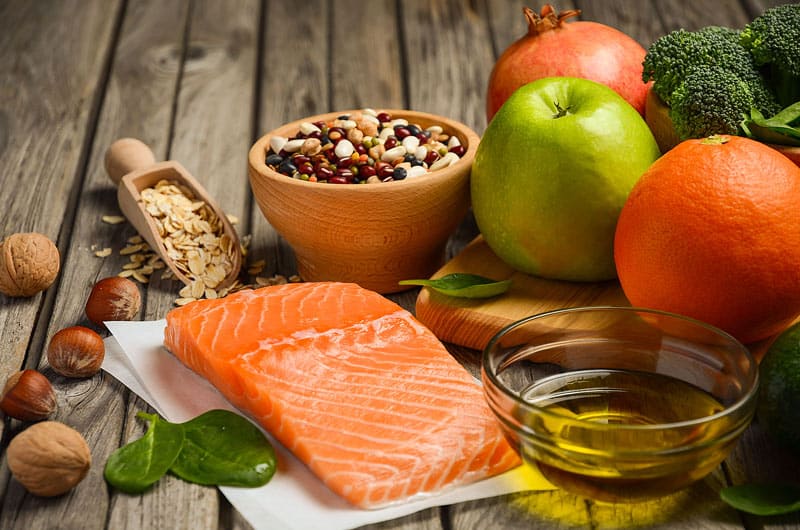
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can help manage asthma. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, reduce airway inflammation. Additionally, fruits and vegetables high in antioxidants, like berries, spinach, and kale, combat oxidative stress, which can worsen asthma symptoms.
The Benefits of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for respiratory health. It modulates the immune response and reduces airway inflammation. Sources of vitamin D include fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and sunlight exposure. Ensuring adequate vitamin D levels can help minimize asthma attacks and improve overall lung function.
Magnesium and Asthma
Magnesium is another vital nutrient for asthma patients. It relaxes the bronchial muscles, making breathing easier. Foods rich in magnesium include dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Including these in your diet can help alleviate asthma symptoms.
The Impact of Allergens and Food Sensitivities
Certain foods can trigger asthma symptoms in sensitive individuals. Common food allergens include dairy, eggs, peanuts, and shellfish. Identifying and avoiding these allergens is crucial for managing asthma. An elimination diet can help pinpoint specific food triggers.
Processed Foods and Asthma
Processed foods often contain preservatives, artificial colors, and flavors that can exacerbate asthma symptoms. High levels of salt and sugar in processed foods can also lead to inflammation. Opting for whole, unprocessed foods is a healthier choice for asthma patients.
Hydration and Respiratory Health
Staying hydrated is vital for maintaining healthy respiratory function. Dehydration can thicken mucus, making it harder to breathe. Drinking plenty of water and consuming hydrating foods like cucumbers and melons can help keep airways moist and reduce asthma symptoms.
Probiotics and Gut Health
Emerging research suggests a link between gut health and asthma. Probiotics, found in yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods, promote a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced gut can enhance immune function and potentially reduce asthma flare-ups.
Conclusion
Diet significantly impacts asthma management. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, ensuring adequate vitamin D and magnesium intake, and avoiding allergens can help control asthma symptoms. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods and stay hydrated to support respiratory health. By making mindful dietary choices, individuals with asthma can improve their quality of life and reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks.